Vitamin D deficiency
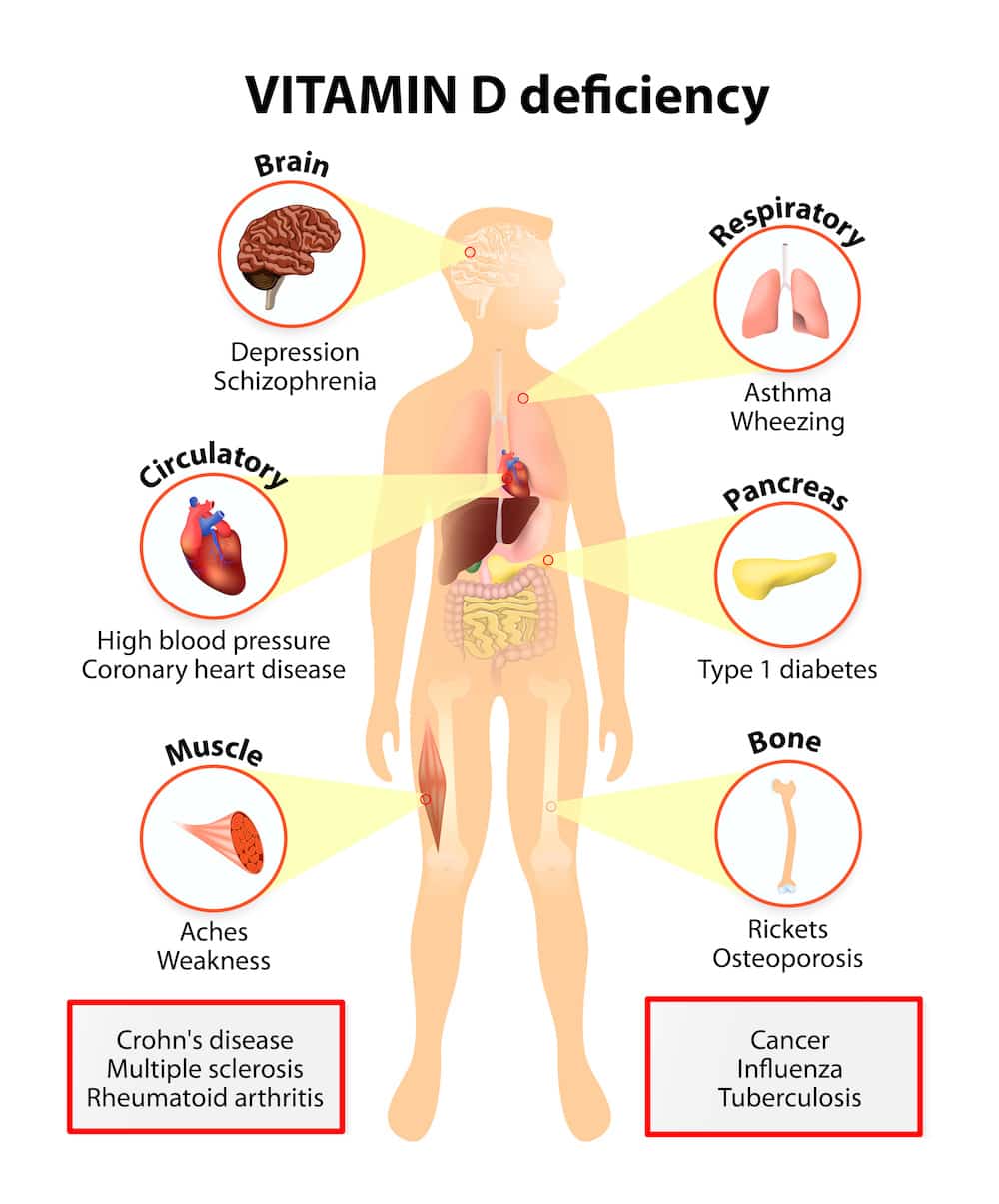
Vitamin D deficiency is a common problem, especially in people who do not get enough sunlight exposure. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to bone problems such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Vitamin D deficiency has also been linked to an increased risk of falls and fractures in older adults.
Vitamin D supplementation is recommended for people at risk for vitamin D deficiency. This includes people who do not get enough sunlight exposure, have dark skin, are obese, have certain medical conditions that affect fat absorption or take medications that interfere with vitamin D metabolism.
Most people can safely take up to 4000 IU daily of vitamin D3 without side effects. Higher doses may be necessary for people with certain medical conditions.
For instance, people with vitamin D deficiency may need to take a higher dose of vitamin D3 to correct their deficiency. People with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, may need to avoid high vitamin D3.
Vitamin D3 supplements are available in both capsules and liquids. The liquid form of vitamin D3 is usually taken with a dropper. Vitamin D3 capsules are typically taken orally with or without food.
Vitamin D3 supplements are generally considered safe. However, like all supplements, they can have side effects. The most common side effect of vitamin D3 supplementation is nausea. Other potential side effects include headache, constipation, and fatigue.
You should talk to your doctor before taking a vitamin D3 supplement, especially if you have a medical condition or are taking medications that could interact with vitamin D3.
