Mumps is a viral disease that spread through respiratory droplets, and ultimately results in swelling of salivary glands. It is a contagious illness caused by paramyxovirus, and causes a systemic disease we can prevent through the administration of a vaccine. Most patients with mumps are pediatric, and it is usually seen with higher incidence during spring season.
It takes 2 to 3 weeks’ time for the virus to show its first symptoms, and this is known as incubation period, which typically last for 12 to 25 days. This viral infection spreads through the saliva or urine and we can detect it after the incubation period by looking at different symptoms we will cover through.
Read Also:
- Fibromyalgia Symptoms: 12 Symptoms of Fibromyalgia (Hard to Believe). What are Yours?
- Shoulder Pain: Overview, Causes and Related Diseases, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Knee Pain: Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment, When To See Your Doctor?
- Low Back Pain: All Things You Want to Know About Low Back Pain Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Home Remedies
- Fibromyalgia: What is Fibromyalgia?, Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- 11 Food Ingredients That Can Cause Inflammation In Your Body To Avoid!
The most important symptoms are as follows:
Salivary Gland Enlargement
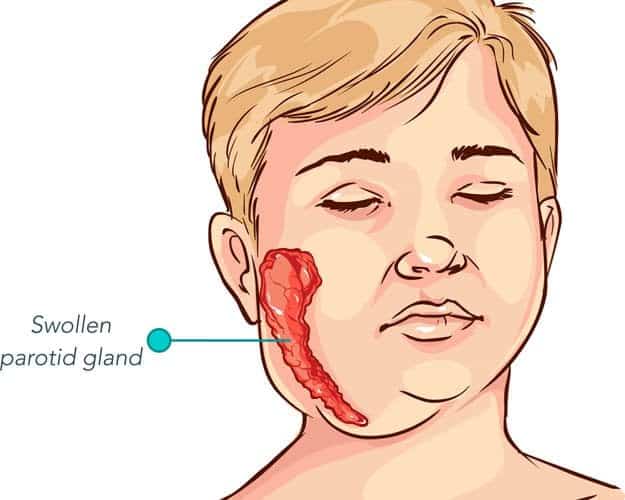
Mumps virus has a tropism for the salivary gland. In other words, even though it distributes throughout the body, it will concentrate and mainly affect the salivary glands. Thus, an enlargement of this area is of the utmost importance.
The area over the parotid gland appears swollen, tender to the touch, and associated with facial puffiness. Usually, one parotid gland enlarges before the other, but unilateral and bilateral swelling may appear. Other Salivary glands such as submaxillary and sublingual glands may also be swollen and tender, but these glands are rarely involved. The parotid glands return to normal in a week’s time.
Trimus
The redness and swelling of the parotid gland may also result in difficulty unlocking the jaw, known as trimus. This symptom may be as severe as to cause problems in day-to-day activities such as eating, speaking, and keeping an adequate oral hygiene. In some cases, it may compromise swallowing, and it becomes a distressing problem for patients, especially younger ones.
Trismus is a prevalent symptom in many different diseases, and your doctor will need to perform a few diagnostic tests to rule out joint problems, periodontal infections, and tetanus infection. You might experience trismus after certain oral surgery procedures, especially after molar extractions, and it is caused by inflammation of the nearby tissues. Thus, if you or your child have this symptom, talk to your doctor as soon as possible and follow his recommendations.
Fever
Fever is one of the most prevalent symptoms, and it may appear before the salivary glands start swelling. In the prodromal state, patients may have a combination of low-grade fever, malaise, and muscle pain, also known as myalgia. This is a very unspecific combination of symptoms that appears in the introductory phase of many different infectious diseases.
In later stages of the infection, patients may experience higher fever that stays throughout the day. In cases of high-grade fever, and especially in younger patients and older adults, it is very important to detect alarm signs and symptoms. Very high fever with vomiting of neck stiffness is not a good sign and may indicate nervous system involvement.
Headache
It is a relevant symptom during the prodromal state and afterwards. Headache in mumps is caused by an increased blood flow towards the head. In these cases, patients should not be worried, because this is very common during infections, and blood flow increases are not a sign of nervous system involvement.
Loss of appetite
In most cases, patients lose appetite and may even lose weight during the infectious and symptomatic phase of the disease. This is especially the case in patients with high-grade fever and more obvious when their intake of water is not in proportion with the amount lost. It is also difficult to chew and swallow due to parotid enlargement, which is why patients tend to refuse eating.
Muscle aches
Also known as myalgia, it is a common symptom in the early phase and later phases of the disease. Patients with an inadequate diet and water intake, existing fever and ongoing viral infection will have fatigue at the cellular level. As a result, they feel always tired and experience muscle aches. Keep in mind this symptom is very unspecific, and most infectious diseases share the same symptom. It is the combination of symptoms that will make the diagnosis.
Testicular swelling
Mumps may result in testicular swelling and tenderness. Around half postpuberal males who get infected with mumps get a condition known as orchitis, where they complain of unilateral or bilateral swelling of the testes. It is not common to reach sterility, but it is a possibility. A much lower proportion of females experience swelling of the ovaries, known as oophoritis, which basically causes abdominal pain, and should be differentiated with pancreatitis.
Abdominal pain
Mumps is the leading cause of pancreatitis in children, and these patients may present with upper Abdominal pain. Pancreatitis pain may also radiate to the upper back. In cases of oophoritis, it would be lower abdominal pain. This is not a common or early symptom, and occurs as a complication of mumps. In these cases, mumps is usually diagnosed by the time abdominal pain starts. Thus, if your children has been diagnosed with mumps and start feeling upper or lower abdominal pain, it is a good idea to talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
Neck stiffness
A physician may check and confirm that the patient has a stiff neck. This is also known as nuchal rigidity, and it is a perceived discomfort or pain when trying to move the neck. It should be differentiated from muscle problems, such as torticollis, which is benign. In complicated cases of mumps, neck stiffness is an indicator of meningitis or any other problem in the central nervous system that requires urgent attention. In these cases, it is usually associated with a very distinct type of vomiting.
Nausea and vomiting
It is very common to have this symptom, often in association with poor appetite, fatigue, and low-grade fever. However, in some cases, nausea and vomiting may become a worrying symptom, especially when vomiting is violent, also known as projectile vomiting. This is a meningeal symptom, one that signals a probable involvement of the central nervous system, and should be evaluated by a doctor as a complication of mumps.
Anemia
Blood levels may decline as a result of the longstanding infection, specifically causing acute hemolytic anemia. This is a condition where red blood cells break down and the patient’s blood reduces the concentration of hemoglobin. This is the protein that gives red pigment and oxygen-delivering function to the blood. Thus, patients with anemia usually have skin pallor and may experience more fatigue than normal in the progression of the disease. Another alteration in blood values is known as thrombocytopenia. It is a decreased platelet count, and it is another complication of mumps.
Flu-like and respiratory symptoms
Mumps patients usually have an associated flu and around half of them experience predominant respiratory symptoms. It is a viral infection and spreads through respiratory droplets, so flu like symptoms usually appear, and become prevalent in the first stages of the disease.
Hearing loss
In some cases, this may occur as a result of infection of the nerves which supply the ear. This is a serious complication in long-standing mumps patients.
Skin rash
A spreading, red and flat rash may start from the face and then spread all over the body in patients with mumps.
Heart problems
Rarely, patients may present with abnormal heartbeat and heart muscle disease. This is because one of the complications is myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle that leads to various alterations and symptoms. Luckily, it is not the most common complication.
Joint pain
Most patients experience diffuse muscle pain, but not all of them report joint pain. In rare cases, mumps can trigger arthritis and arthralgia as a result of severe systemic inflammation. Other rare inflammatory manifestations include mastitis (inflammation of the mastoid bone, located behind the ear) and thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland).
Mumps is a very contagious disease, and complications are more common in adults than children. Thus, it is very important to follow the recommendations by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which includes mumps vaccines in pediatric patients, in the catch-up schedule, and in the adult immunization schedule.
The prognosis of the disease is usually very good, especially in children. Recovery time usually lasts a few weeks, and the most severe complication is encephalitis. Still, mortality rate in cases of encephalitis do not reach 2%. In cases of pregnancy, mumps can lead to fetal death and spontaneous abortions. No malformations have been reported in cases of pregnant women diagnosed with mumps. Another sequela is sterility, which is more common in men with bilateral orchitis.
Read Also:
- Fibromyalgia Symptoms: 12 Symptoms of Fibromyalgia (Hard to Believe). What are Yours?
- Shoulder Pain: Overview, Causes and Related Diseases, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Knee Pain: Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment, When To See Your Doctor?
- Low Back Pain: All Things You Want to Know About Low Back Pain Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Home Remedies
- Fibromyalgia: What is Fibromyalgia?, Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- 11 Food Ingredients That Can Cause Inflammation In Your Body To Avoid!
Treatment for mumps usually includes supportive care to control fever and pain. It may also include cold compresses to relieve pain and inflammation in the parotid glands, and your doctor may require additional tests such as ultrasonography to rule out orchitis. Thus, even if you detect mumps by yourself and understand the basics of treatment, it is imperative to visit your doctor to get a full screening and follow-up of the disease.