Lymphedema is characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in tissues, leading to swelling and inflammation. It typically occurs when the lymphatic system – draining excess fluid and waste products from the body’s tissues – is impaired or damaged. Lymphedema commonly affects the arms and legs but can also develop in other body parts. There are two main types of lymphedema:
- Primary Lymphedema:This type usually occurs at birth or develops later in life due to a congenital abnormality or genetic predisposition. It can manifest at various ages and may become apparent in adolescence or adulthood.
- Secondary Lymphedema:Secondary lymphedema is more common and typically occurs due to damage to the lymphatic system. Common causes include surgical procedures (such as lymph node removal during cancer surgery), radiation therapy, infection, trauma, or other medical conditions that affect lymphatic flow.
Lymphedema can present with various symptoms, and it’s essential to recognize these warning signs to seek early diagnosis and treatment. Here are 12 lymphedema symptoms you should be aware of:
1. Swelling
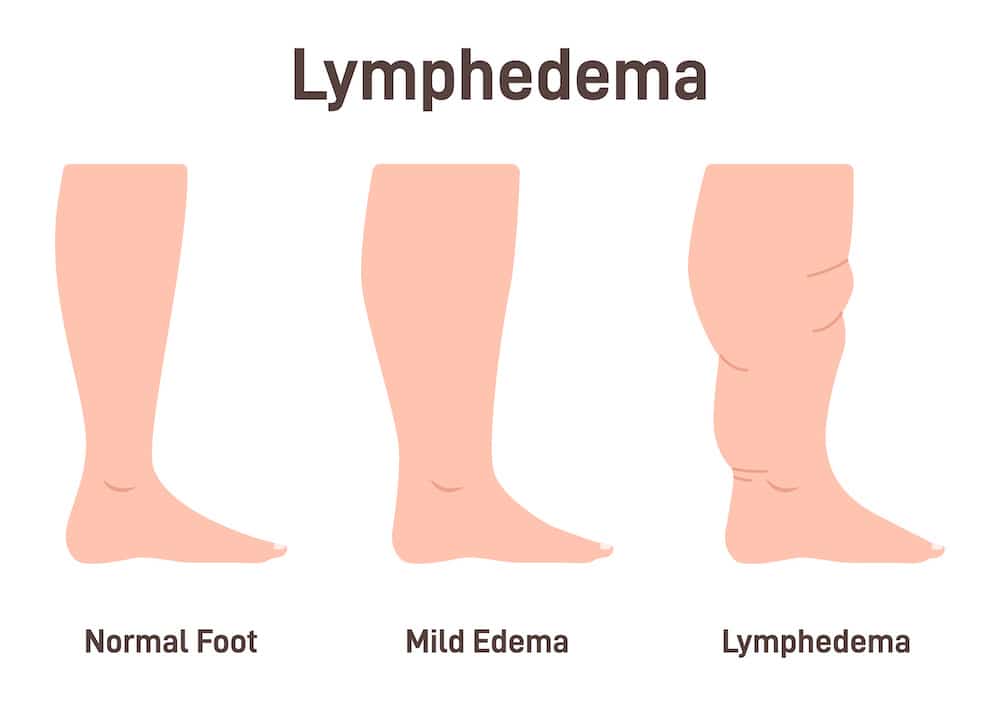
Lymphedema leads to the abnormal buildup of lymphatic fluid in the tissues, which causes the affected limb or area to become visibly swollen. This swelling can vary in severity and may start gradually or suddenly, depending on the cause and individual factors.
Swelling is usually the most noticeable and concerning symptom of lymphedema, prompting individuals to seek medical attention. It’s important to remember that lymphedema is a chronic condition, and early detection and management can help control the swelling and prevent complications.
