What organ would you point out as the most important in the body? It is probably the heart because it only takes a few minutes without a heartbeat to diagnose clinical death. But what about the lungs?
Interestingly, our whole conception of life has to do with the lungs and the function of breathing. Religious people associate breathing with the soul and life itself. Medically, the lungs can’t function without the heart, and the heart is useless without the lungs. That’s why lung cancer is one of the most life-threatening and aggressive diseases a person can have.
Lung cancer is a progressive and uncontrolled growth of lung tissue. This new lung tissue is not useful for breathing and creates an obstruction and then a significant problem for the rest of the body. Since lung cancer is in close contact with blood vessels to exchange blood gasses, the tumor is always in danger of dislodging cells and sending them through the bloodstream. Many patients are detected when lung cancer has already spread to other body parts, which is not a sign of a good prognosis.
Lung cancer divides into two types. They are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer is a type of lung cancer that spreads very rapidly and is very dangerous. Non-small cell lung cancer is a subgroup that includes plenty of lung cancer types. The most common is squamous cell lung cancer. This type of cancer is not as aggressive as small cell lung cancer, but it can also spread if we don’t treat it appropriately.
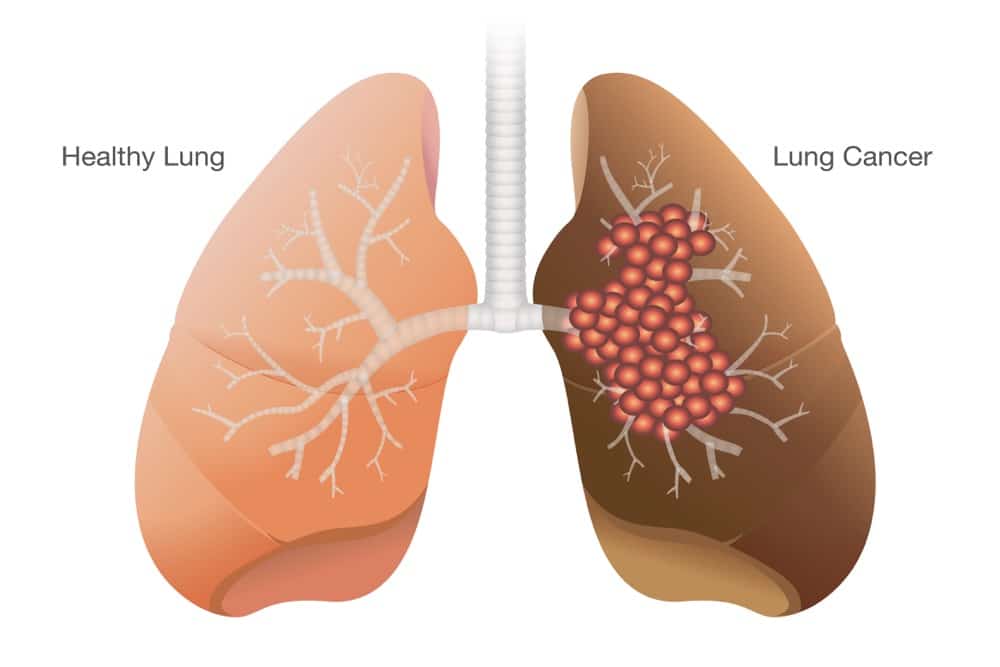
Like other types of cancer, the signs and symptoms of lung cancer can be arranged into different stages. First, we have the early symptoms that correspond to encapsulated cancer. Then, we have other symptoms that arise when cancer grows very large. In another stage, we have signs of metastasis, which can be divided according to the area where cancer spreads.
Initial symptoms of lung cancer
The initial symptoms of lung cancer can last a few weeks in small cell carcinoma or several months in non-small cell carcinoma. It depends on the aggressiveness of the tumor and the overall health of the patient. The initial symptoms are maintained throughout the course of the disease because they are caused by the tumor, regardless of the size. They are usually more severe as the disease progresses.
