Sinus infections are not the same as allergies or bronchitis, but people often confuse the terms and think they are the same. They do have something in common as they involve the respiratory system. But the sinuses are very specific structures we need to understand before studying sinus infection symptoms.
The paranasal sinuses are cavities carved in the skull bones. They are filled with air and lined in a particular type of mucosa made up of ciliated epithelium. The mucosa in the sinuses can produce mucus through small glands, which creates a liquid on the surface that covers the epithelial lining.
We have three groups of paranasal sinuses. They are the ethmoid sinuses, the maxillary sinuses, and the sphenoid sinuses. The ethmoid group is located on either side of the nose. The sphenoid sinuses are found in front of the pituitary gland and behind the ethmoid, in the forehead. The maxillary sinuses are located in the maxillary bone below your eyes.
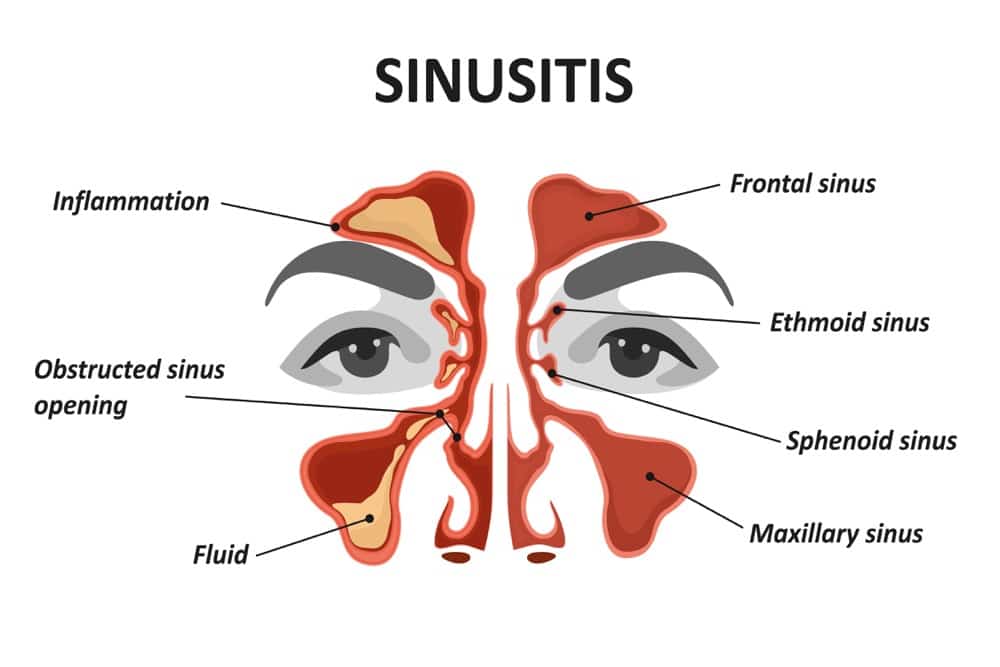
These compartments are linked to each other and to the main airways. Thus, they also communicate with the outside air and are prone to infections. An infection in the sinuses causes inflammation, known as sinusitis. In this article, we will cover the signs and symptoms associated with the infection of these compartments. We will break down the symptoms into acute and chronic sinusitis according to the timeline of the disease.
Acute bacterial or viral sinusitis
As noted above, sinusitis is the inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which happens for different reasons, including an infection. The nasal mucosa is also usually involved because it is connected to the paranasal sinuses. Thus, it is usually referred to as rhinosinusitis.
Acute sinusitis is an episodic presentation of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. It has more distinct signs and symptoms and is sometimes associated with other acute respiratory tract infections. When sinus infections are recurrent and happen more than twice a year, it will be considered acute sinusitis if the symptoms are separated by a minimum of 8 weeks of no symptoms.
The most important signs and symptoms of acute sinus infection include:
