Allergies are exaggerated immune responses against certain particles, bacterial antigens, and even healthy tissue. They are also known as hypersensitivity reactions, and stand as one of the most common types of problems among children and adults. Allergies in children are widespread and can be dangerous sometimes, but in adults they are rarely lethal. Still, certain allergic reactions are more dangerous than others, and anaphylaxis is the most dangerous type, often triggered by food allergy (allergy to peanuts and seafood) or insect bites and stings.
In this article, we are going to cover the most common types of allergies in adults: skin allergies and respiratory reactions. We will also go through anaphylaxis, one of the most dangerous hypersensitivity reactions, and describe the signs and symptoms for each condition.
A-Skin allergies
1. Skin patches
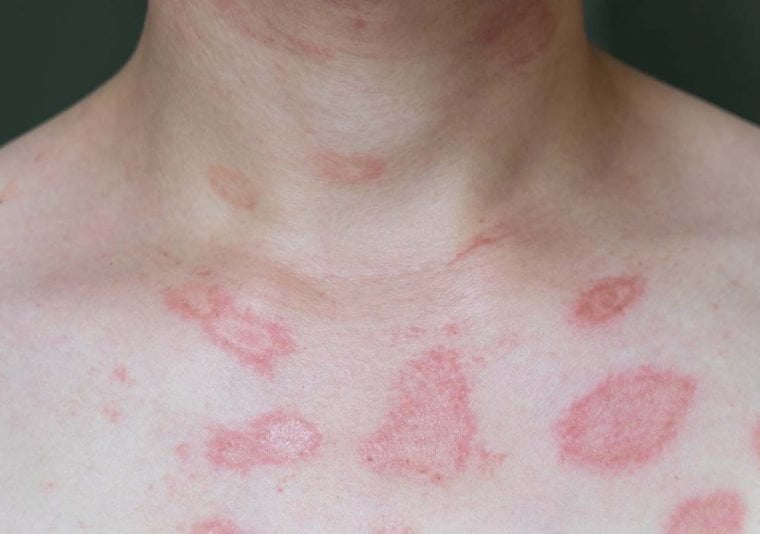
They are commonly seen in adult skin allergies, especially in the case of insect bites and stings. They look like a grown patch with irregular borders, often hot to the touch, reddened and very itchy. Scratching may lead to tearing of the skin or making skin patches grow further and increase the sensation of itching. Thus, it is recommended to use moisturizing and antiallergic creams instead or scratching, and sometimes it will be also necessary to take antiallergic pills to improve this condition and avoid any progression of the allergic reaction.
2. Redness
The skin surrounding the insect bite or sting becomes red and swollen. This is an important part of the hypersensitivity reaction because it is due to an inflammatory cascade triggered by an antigen. The cells in the immune system become activated and start releasing a series of cytokines that dilate blood vessels and make your skin look red and swollen. This color is often associated with a subtle increase in temperature to the touch because the blood is flowing near the skin, and makes it a bit warmer.
3. Itching sensation
The inflammatory cytokines released by the immune cells are also behind the itching sensation that often appears in allergies. This symptom is often triggered by an interplay of interleukins and histamines, and they interact with nerve terminals in the skin and may trigger an itching sensation or hypersensitivity to the touch (a sense of unexplained pain when touching the area)
B-Respiratory reactions
1. Sneezing
One of the most important reactions in a respiratory allergy is sneezing, which is not common in infections of the respiratory tract as it is in hypersensitivity reactions. In a respiratory infection, the antigen that triggers allergies contacts the epithelium of the respiratory tract and is recognized by a series of cells that react against it and trigger an inflammatory reaction along with other recruited cells. The cytokines released by these cells in the nasal cavity and the respiratory tract trigger an itching sensation in the nasal cavity that promotes sneezing.
2. Non-productive cough
Similar to how sneezing is triggered, cough is also common in patients why a respiratory allergy. But different than infections, allergic cough is often non-productive, which means that no sputum or secretion is produced, and when it is, chances are it will not be thick and green but transparent or white and more fluid. This is because, in some cases, allergies trigger production of mucus, but since it is not infected by anything else, it does not become purulent, greenish or foul-smelling.
3. Nasal secretion
Similar to what happens in lower parts of the respiratory tract, respiratory allergies trigger an exaggerated secretion of mucus in the nasal cavity. This secretion is transparent and fluid instead of thick and green, and it is often recurrent and very annoying. Nasal secretion is triggered by the same inflammatory reactions described above, and it is commonly associated with sneezing and postnasal drip.
4. Postnasal drip
This is probably one of the most annoying symptoms of respiratory allergies because it is something we can do nothing about. Postnasal drip is a constant sensation of fluid dripping in the posterior part of the nose. It is caused by an overflow of nasal secretion that is not correctly eliminated by the nasal cavity and starts dripping toward the pharynx and other parts of the respiratory and digestive system. It is often associated with sneezing and the rest of the respiratory symptoms described in this article.
C-Anaphylaxis
1. Lips and tongue swelling
As noted in the section about skin reactions, swelling and skin patches are common signs of skin allergies, but we should be very careful if they are located in the area of the face. Face swelling can be an alarming sign, especially when located in the area of the lips and the eyes. In many cases, this allergic reaction is associated with swelling of the tongue, which feels heavy and bigger than usual, and may even start blocking the throat and causing life-threatening problems. This is one of the first signs of anaphylaxis, and people with known hypersensitivity reactions to foods and insect bites should be extra careful when this symptom appears.
2. Difficulty to swallow
It is mainly associated with swelling in the area of the tongue, and more common in the case of food allergies. In these cases, swelling is not limited to the lips and the tongue. Other parts of the digestive system start to narrow and swallowing becomes difficult and often painful. Even swallowing water and other fluids might feel different and awkward. This is an alarming sign that should be addressed immediately, especially in patients with known hypersensitivity reactions. In some cases, a mild difficulty to swallow may progress into breathing problems as discussed below, and become a life-threatening problem.
3. Breathing problems
It is one of the most feared symptoms of anaphylaxis. Breathing problems or shortness of breath as a result of hypersensitivity reactions can be life-threatening and lead to choking and death in a very short time. This is especially true in aggressive hypersensitivity reactions such as allergies to seafood and peanuts, and these cases should be readily attended in an emergency room because most cases need a careful evaluation, administration of intramuscular or intravenous medications, and much more. Thus, if you feel concerning respiratory symptoms associated with allergies, talk to your doctor as soon as possible and don’t wait for it to become a bigger problem to find a solution.
4. Lightheadedness
Hypersensitivity reactions may also affect our state of mind and levels of alertness and consciousness. Many patients experience dizziness or lightheadedness, and there are some cases of fainting as well, sometimes associated with respiratory symptoms of anaphylaxis. In some cases, patients arrive to the emergency room in a state of confusion that is detected after asking the patient a series of questions about them, where they are, and so on. Thus, if you’re accompanying one of these patients to the emergency room, do not answer these questions to the doctor unless he’s directly addressing you.
5. Vomiting or diarrhea
Hypersensitivity reactions are exaggerated immune responses against a given antigen, and even if they are not related to food or the digestive system, they sometimes trigger digestive symptoms. The most common digestive symptoms in anaphylaxis are vomiting and diarrhea. The reason why vomiting is triggered is because of the inflammatory stress in the body and the release of cytokines to the bloodstream. When they reach the nervous centers that control the gag reflex, patients may start feeling nausea and propensity to start vomiting. Diarrhea is triggered by an inflammatory reaction in the epithelium of the gut, which starts to release water instead of absorbing and leads to watery stools, which may become complicated with dehydration and electrolyte imbalances if not carefully addressed.
6. Bluish coloration of the skin
In anaphylaxis, there are a series of changes in the circulatory system, and one of the most common signs is a bluish coloration of the skin, which is clinically named cyanosis. This condition only reflects a lack of oxygen supply to the area and predominance of non-oxygenated blood, which looks bluish through the skin instead of red. These patients have an impaired circulation of peripheral blood, low blood pressure and low levels of oxygen in the blood, which may lead to serious complications when their condition is not attended in the emergency room.
As you have seen, allergies in adults can be quite dangerous or rather mild and difficult to detect. It all depends on the type of allergy, the antigen involved, and the type of hypersensitivity reaction that is triggered. Most cases of allergies in adults are self-limited and can be controlled by oral or topic antiallergic medications, but you should be careful when symptoms of anaphylaxis start to arise. In these cases, do not delay your diagnosis further and go to the emergency room. That is how your individual case will be examined and you will know for sure whether or not you need to worry about these symptoms. Keep in mind that certain allergens are more rapidly progressing than others, as in the case of peanuts and seafood allergies, and if you have encountered this type of allergy you should be very careful with the preparation of your food and inform the personnel in restaurants about your food allergies before ordering.